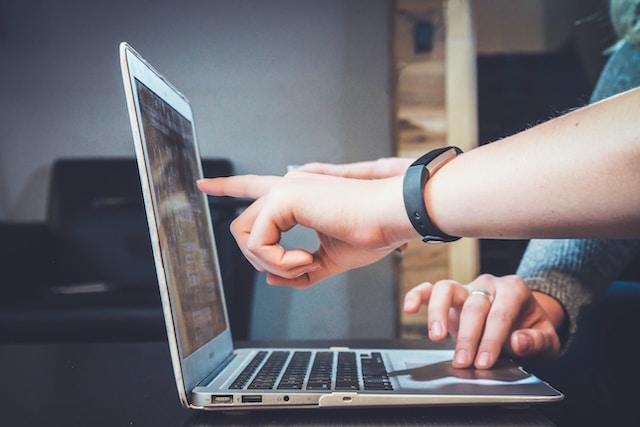
In today's digital age, where the online marketplace is thriving, businesses are constantly seeking ways to gain a competitive edge. Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising has emerged as a powerful tool in the digital marketing arsenal. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of PPC advertising, exploring how it works, its benefits, strategies for success, common pitfalls, and the future trends that are shaping this dynamic landscape.
I. Introduction to PPC Advertising
A. Definition of PPC Advertising
PPC advertising is a form of online advertising in which advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. It's a direct and results-driven approach that enables businesses to place their ads strategically across various online platforms.
B. Importance and Popularity in Digital Marketing
PPC advertising has become increasingly important in digital marketing due to its ability to deliver immediate results. It allows businesses to target their audience precisely and control their budget effectively, making it a staple for many marketing strategies.
C. Purpose of PPC Advertising
The primary purpose of PPC advertising is to drive traffic to a website or a specific landing page. It also aims to convert this traffic into leads or sales, ultimately providing a positive return on investment (ROI).
II. How PPC Advertising Works
A. Keyword Selection and Targeting
PPC advertising begins with selecting relevant keywords that are related to the products or services being advertised. These keywords are used to target potential customers searching for specific terms.
B. Ad Creation and Ad Copy
Compelling ad copy is essential to grab the user's attention. Advertisers must craft engaging headlines and descriptions that encourage users to click on their ads.
C. Bidding and Ad Placement
Advertisers participate in an auction-style bidding system to determine where their ads will be displayed. The bid amount, ad quality, and relevance play a crucial role in ad placement.
D. Quality Score and Ad Rank
Search engines like Google assign a Quality Score to each ad based on its relevance and performance. The Ad Rank is determined by the Quality Score, bid amount, and other factors, influencing an ad's position in search results.
E. Budget Management
Advertisers set a daily or monthly budget for their PPC campaigns. Once this budget is exhausted, the ads will no longer be displayed, preventing overspending.
III. Major PPC Advertising Platforms
A. Google Ads
Google Ads is the most popular PPC advertising platform, reaching billions of users through search and display ads. It offers extensive targeting options and robust analytics.
B. Bing Ads
Bing Ads, powered by Microsoft, provides an alternative to Google Ads with a potentially lower cost per click. It reaches users on the Bing and Yahoo search engines.
C. Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms like Facebook Ads and Twitter Ads allow businesses to advertise to their target demographics with precision. These platforms offer a variety of ad formats, including video and carousel ads.
D. Other Search Engines and Networks
Apart from Google and Bing, there are smaller search engines and networks where businesses can run PPC campaigns, depending on their target audience and goals.
IV. Benefits of PPC Advertising
A. Immediate Results and Visibility
One of the most significant advantages of PPC advertising is its speed. Once a campaign is set up, ads can start appearing in search results immediately, providing instant visibility.
B. Targeted Audience Reach
PPC allows for precise audience targeting based on demographics, location, interests, and more. This ensures that ads are shown to the most relevant potential customers.
C. Cost Control and Budget Flexibility
Advertisers have full control over their budgets, making it easy to scale campaigns up or down based on performance and business goals.
D. Measurable ROI
PPC platforms provide detailed analytics and conversion tracking, allowing advertisers to measure the exact ROI of their campaigns. This data can be used to refine strategies for better results.
E. Competitive Advantage
With PPC, even smaller businesses can compete with larger competitors for ad placement. The quality of the ad and targeting matter more than the budget.
V. PPC Advertising Campaign Strategies
A. Setting Campaign Goals and Objectives
Before launching a PPC campaign, it's crucial to define clear goals and objectives. These could be increasing website traffic, generating leads, or boosting sales.
B. Keyword Research and Selection
Thorough keyword research is the foundation of a successful PPC campaign. Tools like Google Keyword Planner can help identify relevant keywords with the right search volume.
C. Ad Group Structuring
Organizing ads into well-structured ad groups ensures that each ad is closely aligned with specific keywords, improving relevance and Quality Scores.
D. Ad Copywriting and Design
Creating compelling ad copy and visually appealing ad designs is essential to attract clicks and conversions.
E. Landing Page Optimization
The landing page where users are directed after clicking an ad plays a vital role in conversion. Optimizing landing pages for relevance and user experience is critical.
F. A/B Testing and Optimization Techniques
Continuously testing different ad variations and optimizing campaigns based on data-driven insights is key to improving PPC performance over time.
VI. Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
A. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR measures the effectiveness of an ad in getting users to click on it. It's calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the number of impressions.
B. Conversion Rate
Conversion rate indicates how well a PPC campaign is converting clicks into desired actions, such as purchases or sign-ups.
C. Cost Per Click (CPC)
CPC represents the amount an advertiser pays each time a user clicks on their ad. It varies depending on competition and keyword popularity.
D. Quality Score
Quality Score is a metric used by search engines to evaluate the quality and relevance of an ad. Higher Quality Scores lead to better ad placements and lower CPC.
E. Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI is the ultimate KPI for PPC campaigns, measuring the profitability of advertising efforts. It's calculated by subtracting advertising costs from revenue generated.
VII. Common Mistakes and Challenges
A. Click Fraud
Click fraud is a significant concern in PPC advertising, where competitors or malicious actors click on ads with no intention of making a purchase. Advertisers must monitor for and prevent click fraud.
B. Overspending and Budget Mismanagement
Failing to set and monitor budgets can lead to overspending and inefficient campaigns. Regular budget reviews are essential.
C. Poorly Designed Landing Pages
Even with a well-crafted ad, if the landing page doesn't match user expectations or isn't user-friendly, it can lead to high bounce rates and poor conversions.
D. Ineffective Keyword Targeting
Choosing the wrong keywords or failing to update them can result in ads being displayed to the wrong audience or not appearing in relevant searches.
VIII. PPC Advertising Trends and Future Outlook
A. AI and Machine Learning in PPC
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly being used to optimize PPC campaigns, from automated bidding strategies to ad copy generation.
B. Voice Search and Mobile Advertising
As voice search continues to rise, optimizing PPC campaigns for voice search and mobile devices becomes critical for success.
C. Privacy Concerns and Cookieless Tracking
Privacy regulations and changes in tracking technology are shaping how PPC advertisers collect and use data, requiring adaptability and compliance to evolving privacy standards.
IX. Case Studies and Success Stories
A. Real-World Examples of Successful PPC Campaigns
Examining case studies and success stories from various industries can provide valuable insights into effective PPC strategies. We can look at how businesses achieved their goals and overcame challenges through PPC advertising.
B. Lessons Learned from Notable PPC Advertising Campaigns
Analyzing notable PPC campaigns, such as Super Bowl ads or holiday season promotions, can highlight best practices and innovative approaches that can inspire other advertisers.
X. Conclusion
A. Recap of the Importance of PPC Advertising
PPC advertising has proven to be a valuable tool for businesses looking to gain a competitive edge in the digital landscape. Its ability to deliver immediate results, target specific audiences, and provide measurable ROI makes it indispensable in today's marketing strategies.
B. Encouragement for Businesses to Leverage PPC Effectively
As PPC advertising continues to evolve, businesses are encouraged to explore and implement these strategies to enhance their online visibility, engage their target audience, and drive meaningful conversions.
C. Final Thoughts on the Evolving Landscape of PPC Advertising
The future of PPC advertising is promising, with the integration of AI, voice search, and mobile optimization. However, it's essential for businesses to stay informed about industry changes, adapt to evolving privacy standards, and consistently refine their PPC strategies to stay competitive.
In conclusion, PPC advertising remains a dynamic and essential component of digital marketing. When executed effectively, it can deliver significant returns and contribute to the overall success of a business's online presence. By understanding the principles, strategies, and emerging trends discussed in this guide, businesses can harness the power of PPC advertising to maximize their online visibility and achieve their marketing goals.
Remember, the world of digital marketing is ever-changing, so staying informed and adapting to new developments is key to long-term success in PPC advertising.